Lice and their varieties with photos
Content:
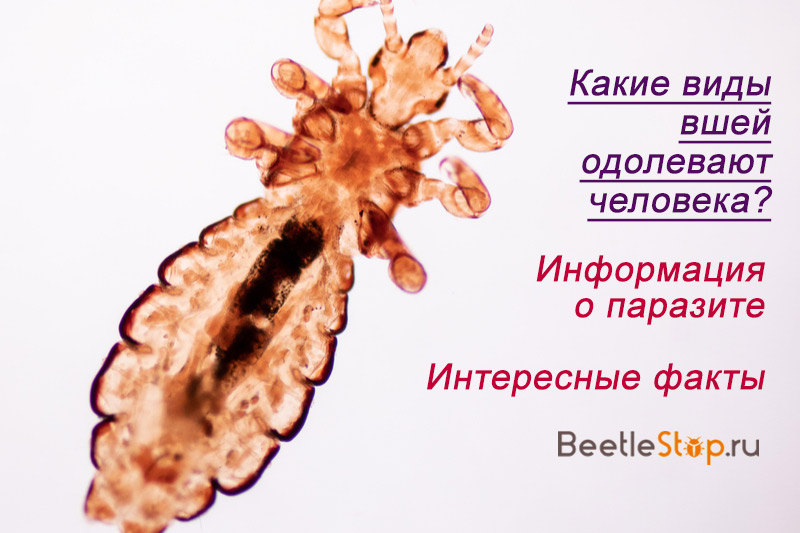
According to statistics, every second person in the world at least once in his life suffered from head lice. Lice have spread all over the world and no one is safe from infection. The transmission of parasites occurs imperceptibly for humans. This can happen in a bus, pool, or even in your home, where households can bring them.
One or two bites can be ignored, but after two weeks dozens of insects will walk on the head, the presence of which will be difficult to miss. What do these creatures look like? Let's take a closer look at them.
Types and classification of lice
Representatives of the suborder of lice belong to the order of the lice. These are small blood-sucking insects that have been parasitizing all their lives on one type of animal. Such a narrow specialization contributed significantly to the classification of parasites, which began to receive names by the name of the host host species. So, for example, there is an elephant louse, squirrel, horse, dog, cat, rat. Inside the animal species, they can change owners, but, as a rule, they never go beyond it. Only a few sometimes change this rule, but do it only as a last resort and whenever possible try to switch to "their" animal.
Human lice can only live in public. They adapted to his lifestyle, developed protective devices.
Types of Human Lice:
- head
- wardrobe
- pubic.
Many scientists consider the head and wardrobe to be two subspecies of the same species - human lice. Head louse lives only on the scalp. Wardrobe - in the folds of clothes. Although they have some differences in structure and lifestyle, they can still interbreed and even give viable offspring. Pubic lice can be found on the entire surface of the body, where there is hair, but prefers the intimate area. She is not adapted to life on her head.
Parasites on animals are not always lice. The detachment of poo-eaters includes insects that feed on hairs, down, feathers and other skin derivatives. They are called so - poohoedy. Mostly they parasitize on birds, but are also found on animals. Lupus and lice are very similar in appearance, but have a completely different structure of the oral apparatus. In lice, it is piercing-sucking, in lice-suckers - a gnawing type.
Appearance and structure
The body of the louse has undergone strong changes in the process of evolution. It acquired the typical features of parasites - hooked legs, flat shape, inconspicuous color. Depending on the type of the host, the appearance may vary slightly, but in general, all lice are similar to each other.
How do they look?
What do lice look like? Outwardly, these are very small insects with three pairs of tenacious paws equipped with claw-shaped claws at the ends. Like bugs, their body is flattened in a horizontal plane. The head and chest are relatively small, the abdomen is voluminous and long. The body length of these parasites can range from 0.4 mm to 6 mm. A kind of giants can be considered an elephant louse - 6 mm. The average size of the pubic louse is 1.5 mm.
What color are lice? Basically, these insects have an inconspicuous grayish-brown color. Such a skin helps them hide in the hairline. There are whitish and yellowish specimens and even almost devoid of pigment, in which all the insides are visible through the transparent skin.
Interesting fact! Lice in dark-skinned people over time acquire a dark color. Asians - yellowish. Among Europeans, gray, translucent lice, almost devoid of pigmentation, are mainly found.
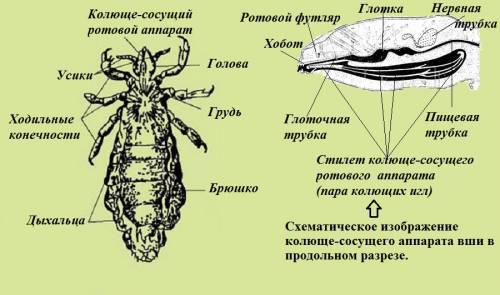
Lice structure
The body of lice is a prime example of a parasitic lifestyle. Everything in it is adapted to cling and suck blood. It differs slightly from poohovers. So, for example, in lice, the oral apparatus has a piercing-sucking structure. The upper jaw and lower lip are hard sharp stilettos with which the parasite pierces the skin. Between them is a long proboscis, through which the insect sucks blood from the body of the victim. At the time when the louse is not feeding, the stilettos and proboscis are removed in a special cavity - the vagina located inside the head of the parasite.
The following structural features of the body of lice are also interesting:
- short but very tenacious limbs;
- claw hooks at the ends of the legs;
- a skin fold around the mouth with hooks, with the help of which the parasite is held on the host’s body during eating;
- lack of wings;
- respiratory openings on the sides of the body.
The structure of the genital organs is also remarkable in lice. In females, they are represented by paired ovaries with oviducts, a testis, and an unpaired excretory passage. The holes of the glands that produce a sticky secret go into it. At the end of the abdomen there is a bifurcation that helps to hold the hair during egg laying. The male is equipped with testes, vas deferens and the copulative organ, with the help of which he introduces the seed into the body of the female.
The sensory organs are represented by a pair of sensitive antennae and two small eyes of simple structure. Lice's vision is weak, and it doesn’t need it. She receives all the information she needs through touch.
Lifestyle
Lice are parasites with a rather interesting way of life. They never leave the body of their master. Their entire life cycle takes place only on it. They feed, breed and lay their eggs on the animal on which they were born. They voluntarily leave it only in very rare cases, since they are completely unsuitable for life outside of it.
Lice feed exclusively on blood at all stages of their development. Their body is simply not able to accept anything else, since it is adapted to absorb only liquid food. They feed quite often. Sometimes up to 6 times a day. This voracity is explained by the intensive growth of larvae and high fecundity.
The lice have a short life span of just over a month. However, during this time, the female manages to lay several tens and hundreds of eggs, of which, after 1-4 days, the voracious larvae hatch. After a couple of weeks, they themselves already begin to lay their eggs.
How does infection happen? Are lice jumping or not? Oddly enough, they really jump. However, this is quite specific. They swing in the balance, like on a swing, and then unhook and fly to another head in the vicinity. Also, infection is possible through the joint use of hair care products - combs, hairpins, elastic bands. You can also pick up lice in the pool or on the beach if a person with a head lice bathed in the water before.
Interesting fact! The higher the human body temperature, the faster the larvae hatch from nits and develop into an adult insect. True, in this case, their overall life will be reduced.
What are they needed for?
Why did lice appear? Why do they need nature at all? Surely such a question was asked by everyone who happened to encounter them. All living things are useful in some way. Each animal and insect plays a role in the biosphere of the planet.What about lice? Does lice have any meaning in nature?
There is an assumption that these parasites at the beginning of their existence were included in the food chain. Perhaps they were larger and more nutritious than now. Over time, they became smaller and at one point fell out of the public life of the planet. Now it’s just parasites. Harmful and certainly not needed by anyone.

Interesting facts from the life of lice
If you put aside the squeamishness that people experience when meeting with these parasites, you can find out a lot of interesting things about their life. Here, for example, are just some interesting facts about lice:
- These parasites do not like to leave their owners and if you give them a choice, among all other people they will choose the one on which they were born.
- Best of all they live on a clean head. It is more difficult to move through oily and dirty hair, nits do not stick to them, and skin devoid of sebaceous secretions is easier to bite through.
- By the distance at which the nits are from the roots of the hair, you can determine when the infection occurred. For a day, hair grows about half a millimeter, and lice lay their eggs at the roots. Thus, the distance from the root to the nits is 1 cm, an indicator that parasites have been living on your head for a month now.
- Lice are no worse than cockroaches able to develop resistance to pesticides. New species have already appeared that are not sensitive to conventional preparations for these insects.
- Lice are contemporaries of dinosaurs. During the excavations, paleontologists discovered a louse that lived 44 million years ago!
- The lightest insect in the world was recognized as a male of striped lice. It weighs approximately 0.005 g.
- As scientists found out, human lice appeared at the same time when the paths of humans and monkeys began to diverge. This is confirmed by the fact that modern parasites can live on chimpanzees, although if they have a choice they will still prefer people.
Interesting facts about lice and head lice can be found in this video:



 (votes: 5, average rating: 3,40 out of 5)
(votes: 5, average rating: 3,40 out of 5)