Types of ticks - a neighborhood that we do not notice
Content:
Ticks (in Latin Acari) are the largest group in the arachnid class. There are 54,000 species. They settle in soil and water, on plants, animals and humans. Acarology is engaged in the study of ticks, among its areas is medical, agricultural and veterinary. Parasitiform forms of ticks are carriers of dangerous diseases transmitted through bites. Other arthropods damage crops and food. Studying the characteristics of these small animals helps to find effective ways to destroy them.

Appearance and classification
Ticks are the oldest invertebrates with a primitive structure. Miniature body size helps them to spread everywhere and survive. Their body is divided into two parts, the border is closer to the front. Four pairs of legs consist of several segments, the final is the foot, armed with claws and suction cups.
Information. Adults have 8 legs, and larvae have 6.
The first pair of appendages - chelicera or jaw, is characteristic of all arachnids. They look like ticks and are used for piercing and cutting. Also in the oral apparatus are pedipalps, limbs located on the side of the chelicera. These processes and grow together at the base and together with other parts form a movable head. Some differences in the structure of the oral organ are observed, depending on the type of nutrition. In saprophages eating dead remains, it is gnawing, and in predators and parasites it is prickly-sucking.
In representatives of different species, the number of eyes varies from 0 to 5. The body of arthropods can be soft, leathery or covered with a hard shell.
Classification
Most species of ticks are predators and saprophages. They live independently, for development they do not need to parasitize on other individuals. Scientists divide the Acari subclass into three suborders:
- Hay mites (Opilioacaridae) are large ground individuals 1-3 mm in size. There are 25 known species inhabiting the tropics and subtropics. Their head and thoracic region merge into the cephalothorax, delimited from the abdomen. The oral apparatus consists of chelicera, pedipalp and upper lip. From the back there are three pairs of eyes. Long legs make them look like haymakers. Representatives of the family live in the forest, under the stones, in the soil. They feed on solid foods, small arthropods, plant pollen and fungal spores in the diet.
- Parasitiformes ticks (Parasitiformes) - superorder numbering 12.5 species. This group includes vertebrate parasites, as well as predators and saprotrophs (individuals that destroy the remains of living creatures). Among the most dangerous representatives of the superorder are ixodic and argus ticks.
- Acariformes ticks (Acariformes) - the largest group, which includes more than 30 thousand species. For individuals of the family, the completion of segments during life is characteristic. About half of the group are sarcoptiform ticks parasitizing on vertebrates. They feed on feathers, skin, hair. Thrombidiphomic ticks (almost 22 thousand species) include plant pests and carriers of infectious diseases.
Attention. Diseases transmitted to humans and pets from ticks are called acarises.
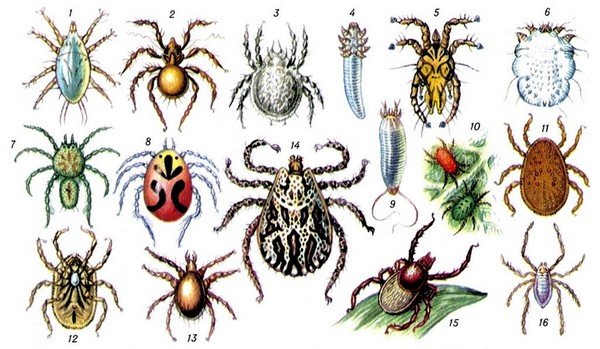
Life cycle
Depending on the species, arachnids significantly differ in life expectancy and stage of development. Reproduction occurs sexually. The female is often larger than the male, which in many species dies after fertilization. Typical phases of tick life are:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph;
- adult individual.
The average individuals live from several weeks to months, but there are long-livers. These include ixodid and carapace mites. In winter and under adverse conditions, arthropods fall into diapause, a state of slowing down of all processes that allows you to survive without food.
Species diversity
What are the ticks, what do they eat and where do they live? These questions are asked by beginning entomologists and just nature lovers.
Saprophages
The group of saprophages includes a large number of ticks. They feed on organic residues and do not pose a threat to humans. The way of life and meaning in nature is similar to earthworms. Saprophages contribute to the formation of soil humus. A typical representative of this group is the carapace tick (oribatid). This is the dominant species that can be found in forest soil. Their number reaches hundreds of thousands of individuals per 1 m2. The sizes of adults are 0.7-0.9 mm, their body is black.
Oribatids are an important link in the soil food chain. Carapace mites show a slow metabolism and development. The life cycle from an egg to an adult takes from several months to 2 years.
Attention. Some types of helminths parasitize the body of oribatid, eating grass with ticks, animals can become infected with tapeworms.
Phytophages or plant mites
Among arthropods, many species feed on plant sap or their debris. Phytophages are pests of indoor plants and agricultural crops. Their habitat is leaves, buds, roots, bulbs. What types of ticks can be found on plants?
Pests feed on the plant cell sap, they bite into the tissue, pierce the leaves. General damage contributes to the drying and death of crops. Spider mite the most famous parasite on indoor plants and agricultural crops. Due to the small size of 0.3-0.5 mm, it is not immediately noticed on plants. The consequences of his life are spots on the leaves and the appearance of cobwebs.
Ticks live in colonies, hiding on the back of the leaves. Favorable conditions for their development is a temperature of 27-280 and low humidity. The juice of plants feeds on larvae and adults. In the absence of treatment with acaricidal preparations, the spider mite can destroy the entire crop. On indoor plants, in addition to the ordinary spider mite, other species can be found: red, atlantic, red-legged.
Gall tick - representatives of the family of dangerous pests of forest trees and cultivated plants. They settle on apple trees, plums, pears, grapes. They differ in small size - 0.1-0.3 mm. The body is spindle-shaped, there are four legs. Pests suck juice from tissues, causing deformation and the formation of galls (pathological formations on the leaves, roots and other parts of plants).
Barn
This group of ticks feeds on solid foods - grain, flour and other products. Barn ticks are viable and widespread. They settle not only in places of storage of human stocks, but also in burrows of animals. They can be found in the soil, on the roots of trees, in mosses, in the aerial parts of plants.
Flour mite eats cereal seeds, sunflower seeds, dried fruits and vegetables, cheese. Body size from 0.2 to 0.5 mm, transparent color. If ingested, it causes poisoning; if inhaled, an asthmatic reaction occurs.
Water inhabitants
Water mites have a rounded body and elongated legs with bristles, this structure contributes to swimming.Larvae parasitize on mollusks and aquatic insects. The development of ticks is unusual, there are two phases of the egg - primary and secondary, the larvae also go through two stages - six-legged and eight-legged. Representatives of this family are often painted in bright colors.
What species are dangerous to humans?
Getting into the human body, ticks cause damage to the skin, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system. They cause allergies, parasitic diseases, and infections. The pathogenic effect on humans has many manifestations, they are divided into three groups:
- acarodermatitis - allergic manifestations on the skin caused by contact with ectoparasites;
- deep acarises - diseases provoked by endoparasites, for example, scabies itching;
- tick allergies.
Tick-borne infections transmitted by bite are considered separately. Parasites feed on blood, while infecting the host with dangerous ailments:
- Tick-borne encephalitis is a viral infection with fever, intoxication, damage to the brain and spinal cord.
- Relapsing fever - the disease proceeds with alternating bouts of fever.
- Tularemia - damage to the lymph nodes, intoxication, organ enlargement, prolonged fever.
- Lyme Disease - one of the common pathologies spread by ixodid ticks. The defeat affects the heart, nervous system, eyes.
- Different types of fever - Tsutsugamushi, Marseille, hemorrhagic.
Dangerous tick species include:
Ixodic
The leader among the types of dangerous ticks are ixodic parasites. They spread several dangerous infectious diseases, including encephalitis. The family has about 650 species, their distribution even captures the Arctic, where parasites live on penguins. The genus Ixodes includes two representatives that are carriers of encephalitis in Russia.
Taiga tick distributed in the taiga zone, and also captures the Moscow, Leningrad region and Karelia. Habitat from Western Europe to the Pacific Ocean. This species is a polyphage - it feeds on reptiles, mammals and birds. Adults climb to a height of 1 meter and up to 7 days lie in wait for the victim on forest paths. It is found in the city zone and in summer cottages. The development cycle is 2-3 years. The taiga tick is active at a temperature of 1 to 200. The peak of activity is May-June.
Attention. A tick captures the smell of a person at a distance of 10 m, so their accumulation is observed along the paths.
Types of ixodid ticks are very similar to each other, only professionals can distinguish them.
The dog tick has an oval body with a shield on its back. In males, it covers the whole body, and in females and nymphs, only a small part. This structure allows the body of the parasite to stretch when it is fed, increasing several times. Distribution area - Europe, Asia, North Africa and America.
For some types of parasites, specificity in the choice of the host is characteristic, ixodid ticks feel great on all types of animals and on humans. The size of the hungry female is 3-4 mm, the male up to 2.5 mm. After saturation with blood, the female increases to 10-11 mm. They need a large amount of nutrients to lay thousands of eggs. Not everyone survives, 1 mm long come out of the remaining ones. For further growth, they need to find a host.
Attention. If the larva appeared in the autumn, then it will continue its development for the next year.
Larvae feed on rodents; after feeding, they molt and turn into a nymph. At this stage, they suck the blood of larger animals, it takes 4 weeks to become an adult. At any active stage, they are carriers of vector-borne diseases.
How to get rid of a tick
With a bite of a bloodsucker, first aid should be given to a person. The parasite is taken out carefully, trying not to crush, because this increases the chances of infection. Surgical gloves are recommended. You need to get the female with tweezers or a special device.Ticks are taken out in a circular motion counterclockwise. The bite site is treated with an antiseptic. The condition of the bitten must be closely monitored, if dizziness, aches, fever should be addressed to the hospital.
Attention. Only a small percentage of ixodid ticks transmit the disease when bitten. To exclude or confirm the likelihood of an ailment, you can send the parasite for analysis to the laboratory.
Precautionary measures:
- vaccination from encephalitis to the tick activity season;
- walks in clothes covering hands and legs, wearing a headgear;
- examination of the body after hiking in the forest, the parasite needs time to suck;
- processing clothes and body acaricidal compounds and repellents.
Subcutaneous
Demodex refers to opportunistic organisms. This is one of the types of ticks that people have. His stay in the human body is considered the norm, but with a decrease in immunity, uncontrolled reproduction begins. Ticks that parasitize humans and pets, with an increase in the number, cause itching and provoke inflammatory processes. This is one of the smallest arachnids, its size is up to 0.3 mm. Habitat - hair follicle.
Parasites cause a skin disease on the face called demodecosis or acne. Ticks in the process of life emit harmful products that contribute to the appearance of an allergic reaction and acne. The disease is transmitted between people through direct contact.
Scabies
Superficial dermatoses cause several types of ticks. Usually people become infected with parasites from the body of animals and birds - rats, pigeons, hens. These mites do not bury themselves in the skin, but simply apply bites that cause itching and blistering. Parasites hide in underwear and bedding. It will require treatment with an antipruritic agent (salicylic alcohol) and disinfection of linen and premises.
Itchy itch is an intradermal parasite that causes a specific disease - scabies. Females make moves in the epidermis and lay 2-4 eggs daily. The length of the female is 0.45 mm, the male is 0.23 mm. Sharp bristles on the legs of the parasites, helping to move in the thickness of the skin. Outside the body, they can live up to 3 days, quickly die in the cold and when boiled. The female's life span is 4-6 weeks, the male dies after mating.
Larvae emerge from eggs after 3-4 days, they immediately begin to dig their moves. After 2 weeks, these are adult sexually mature individuals. At night, the females are selected on the surface of the skin to move and mate, at this moment the likelihood of infection. Parasites can settle on any part of the body, but prefer the back of the hands, armpits, the area between the fingers. Scabies mites feed on blood, causing severe itching. Combing areas are often inflamed.
Attention. For the treatment of scabies, topical preparations are used that kill adults and eggs. These are acaricides based on benzyl benzoate and sulfur.
Bed
Dust or bed mites are synanthropic organisms. Their existence is inextricably linked with man. The microscopic size of arachnids 0.1-0.2 mm does not allow them to be detected without special devices. The life cycle is 65-80 days, the most favorable temperature is from 18 to 250 and humidity 55%.
Their habitat is pillows, blankets, upholstered furniture and toys, curtains and slippers. Bed mites do not drink human blood, they feed on dead pieces of the epidermis. The danger is represented by proteins in the stool of the parasite, causing a persistent allergic reaction. It manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- itching
- redness of body parts;
- sneezing
- trouble breathing
- inflammation of the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Attention. According to statistics, 70% of children have asthma. allergic reaction to dust mites.
The control of parasites includes the use of special means and preventive measures.Anti-acaricidal compounds are added to water when cleaning the premises and when washing clothes. These include:
- Easy Air Liquid - a product made from natural ingredients that destroy ticks in bed and dust;
- Accaritox powder, valid for up to two weeks. The insecticidal composition is dissolved in water until a stable emulsion.
- Aerosol "Milbiol" is a preparation for processing pillows and upholstered furniture that destroys parasites.
- "Tsifoks" - acaricylum concentrate for disinfection.
- Allergoff - a line of drugs that effectively destroy bed mites. It has a neutral smell, has a persistent acaricidal effect.
Argasovy
Representatives of the Argas tick family have soft integuments and hide in secluded places - burrows, grottoes, crevices and caves. Their length is 3-30 mm, the color is gray, after feeding with blood it changes to purple. Individuals parasitizing on cats and poultry are called agazidoses. There are 12 types of mite ticks that bite a person. Their attacks are invisible, manifested by redness and the appearance of a papule. Due to severe itching, a person combes a wound and inflammation occurs.
Parasites carry the causative agents of relapsing fever, Q fever, plague and other diseases. Their saliva is toxic, its ingestion can cause a strong allergic reaction. Among the dangerous species:
- Persian;
- Caucasian;
- township;
- conch.
Information. Argasids are able to starve for 11 years.
Parasites are harmful to animal health; they die without proper treatment. Ticks are active at night, in the absence of other hosts attack a person. The bite is painful, therefore immediately noticeable. In this case, you must immediately go to the hospital.
Gas
Representatives of the Gamasina family have a body size of about 1 mm, individual species reach 2.5-5 mm. Among them there are freely living and parasitic forms. The latter settle on mammals, insects, snakes, birds. The oral apparatus of the parasites consists of a proboscis for penetration into the skin of the host and chelicera for piercing. In its development, gamasid mites go through 5 stages:
- egg;
- larva;
- nymph 1;
- nymph 2;
- adult individual.
Life expectancy is 7 months.
Parasites live in soil, manure, on the bark of trees, in cracked asphalt. They can settle in the house if they do not adhere to sanitary standards. For humans, parasites living on rats and mice are dangerous. Together with rodents, they penetrate into the home. Parasites are carriers of rat and mouse tick-borne dermatitis. Their bite often causes an allergic reaction of varying intensity. Another variant of infection is from birds living next to humans.
This order includes the predators Phytoseiidae, used in the fight against plant pests. Ticks 0.2-0.8 mm in size are natural regulators of the number of phytophages. Their body is oval, it is covered with bristles. For movement, 4 pairs of legs are used. A popular type of predatory family - phytoseyulus is available for the destruction of spider mites in open, covered ground (in greenhouses). Its color is from orange to cherry. The male is smaller than the female; it can only be examined under a microscope.
Information. Predator nymphs destroy spider mite eggs, which are insensitive to many insecticides.
Mites
The Trombidiodea family stand out among other arthropods in bright colors. They grow to sizes of 3-5 mm. At the stage, the larvae are parasites; adults are predators. Larvae settle in the skin of reptiles, birds, mammals. The beetle can be seen in the spring while working in the garden. They prey on insects. Some species are capable of transmitting Japanese river fever to humans.
A variety of tick species is part of nature. Only a small part of these small animals is dangerous to humans. Most of them, due to their microscopic dimensions, remain invisible to us.


 (votes: 8, average rating: 4,50 out of 5)
(votes: 8, average rating: 4,50 out of 5)