What is a tick bite dangerous?
Content:
In the spring-summer period, the probability of getting a tick bite is significantly increased. This should be taken very seriously. Bloodsuckers are the carriers of certain infections that are dangerous to human life and health. Every year, almost half a million Russians turn to medical institutions for parasite bites, many of them children. How many cases remain unregistered is unknown.

Tick Overview
Ticks are characterized by seasonality. The first cases of attack are recorded in early spring, when the air temperature rises above 00 C, and the latter in the fall. Peak bites occur from April to July.
Bloodsuckers do not like the bright sun and wind, so they watch for their prey in humid, not too shady places, in dense grass and shrubs. Most often found in ravines, at the edges of the forest, along the edges of paths or in parks.
Sensing the victim, the tick raises the front legs and actively moves them, trying to cling to clothes. He does it very deftly, suction cups and hooks located on the forelimbs help. During the bite, parasites inject an anesthetic, like mosquitoes, so suction goes unnoticed. Favorite places for a bite are the neck, the area behind the ears, the armpits, the inguinal zone, the elbow bends.
Attention. Not all ticks are carriers of disease. But even sterile parasites, and such 85–90%, can cause allergic reactions.
For complete saturation, the male bloodsucker needs an hour, the female needs several days. In choosing the object of hunting, parasites are not picky, bite everyone who comes in the way - birds, small and large animals, humans.
Tick attack and bite
The tick gnaws through the skin with the help of a hypostome (oral apparatus) studded along the edges with backward growths. This structure of the organ helps the bloodsucker to hold firmly in the tissues of the host.
If the tick is a carrier of encephalitis, the pathogen concentrates in the salivary glands of the bloodsucker and enters the body of the victim at the time of the bite. Therefore, even the immediate removal of the sucked parasite does not reduce the risk of infection. In the case of Lyme disease, the virus accumulates in the digestive tract of the tick and enters the body when it begins to eat, that is, 5-6 hours after suction. In this case, early removal of the parasite can save from infection.
Redness of the skin at the site of the bite does not mean infection. A color change may appear on the background of an allergy or a parasite that has not been found for many hours in the victim’s body. The reaction of the body to a tick bite can be seen in the photo. If such symptoms appear, it is better to consult a doctor.
In borreliosis, a tick bite looks like focal erythema up to 20-50 cm in diameter.The form of inflammation is most often correct, with an outer rim of bright red color. After a day, the center of erythema turns pale and acquires a bluish tint, a crust appears and soon the bite site is scarred. After 10-14 days, there is no trace left of the lesion.
Tick Bite Signs
Most often, a sucking parasite is not immediately noticed. Several hours pass before the victim begins to feel unwell and realizes to examine himself. The first symptoms of a tick bite in a person appear as follows:
- weakness, desire to lie down;
- chills and fever, fever;
- photophobia appears.
The dynamism of the signs depends on the number of sucking parasites and the characteristics of the victim's body. The bite symptoms are especially pronounced in people of old age, children and suffering from allergic reactions or immunodeficiency pathologies.
Attention. In people of this group, the symptoms can be supplemented by low blood pressure, increased heart rate, itching, headache and an increase in nearby lymph nodes.
In rare cases, difficulty breathing and hallucinations are observed.
Temperature after a bite as a symptom of a disease
An increase in body temperature in the first hours after a tick bite most often does not mean anything serious. So an allergic reaction to the bloodsucker saliva is manifested. You should be wary if a fever appears a few days after the suction of the parasite. Such a reaction of the body may indicate the onset of the disease.
Each infection caused by a bite of a bloodsucker has its own characteristics:
- With tick-borne encephalitis, a relapsing fever appears. The first temperature rise is recorded 2-3 days after the bite. Two days later, everything returns to normal. In some cases, a repeated increase in temperature is observed for 9–10 days.
- Borreliosis is characterized by fever in the middle of the disease, which is accompanied by other symptoms of infection.
- With monocytic ehrlichiosis, the temperature rises 10-14 days after a tick bite and lasts about 3 weeks.
Almost all diseases transmitted by bloodsuckers are accompanied by fever.
Tick Bite Code of Conduct
So what to do if a tick has bitten? First of all, it is necessary to remove the bloodsucker as soon as possible. This should be done slowly and carefully so as not to damage it and not provoke infection. At the same time, gasoline, nail polish and other chemicals cannot be used. Vegetable oil or fat will not help either. It is better to use effective and proven methods.
Tick removal by thread
The method is simple, but requires a lot of dexterity and patience. It will be useful when extracting large individuals. In order for the procedure to succeed, it is recommended that you follow these steps:
- Take a long and strong thread
- Tie a loop at the border of the skin and body of the parasite and carefully tighten it.
- Rotate, sway and sip counterclockwise to slowly remove the tick.

The removed bloodsucker must be placed in a glass container with a tight lid and taken to a laboratory for research.
Removing a tick with tweezers
Another easy way to get rid of a tick. With tweezers, you can remove a bloodsucker of any size. The main manipulations in this case are similar to the option of pulling the thread. Tweezers are best used with flat edges, capturing the parasite at the base. Then, with careful rotational movements, remove the tick and disinfect the wound.
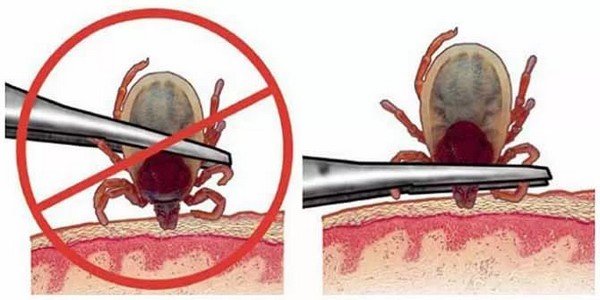
Attention. During the removal of the bloodsucker, the tweezers must be held strictly parallel or perpendicular to the skin.
Tick wrenches
Not so long ago, the pharmaceutical industry launched the production of special devices for removing the parasite.The kit includes two tools - large and small for ticks of different sizes. With the help of a twist, the parasite can be quickly and efficiently removed without damaging it.
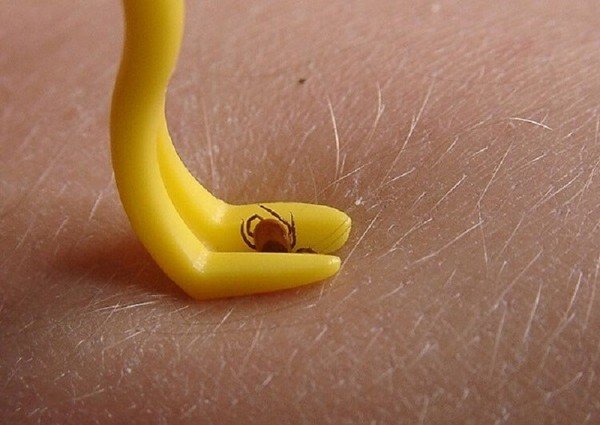
The kit includes a test tube, in which it is recommended to place a live parasite and keep it in the refrigerator for further research.
Other tick removal methods
If there are no devices nearby during a tick bite, you can try pull out the parasite with your hands. The method is risky, but if done correctly, the result will be good. In this case, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Wrap your fingers in a handkerchief or gauze to make it easier to hold the tick.
- Grab it at the very border with the skin and gently twist it out.
- Disinfect the wound or rinse with water.
If for some reason the tick cannot be saved for analysis, it should be destroyed by pouring boiling water or burning on fire.
Often you can hear the advice of "experienced" people to remove bloodsucker with oil. Despite its apparent simplicity, the method is not only useless, but rather harmful. The parasite, sensing a threat to life, will relax the proboscis and burp the contents of the stomach along with pathogens back. In this case, the risk of infection will increase sharply.
Attention. If you can’t remove the bloodsucker yourself, you must contact the nearest emergency room.
Medical workers will provide first aid for a tick bite: they will professionally remove it and send it for examination, the wound will be disinfected and they will tell you how to behave further. The doctor will inform you which symptoms should be addressed in the coming month.
What to do after removing the tick?
In people who are prone to allergies, a tick bite can cause a strong body response. Often, facial swelling develops, difficulty breathing and muscle pain. In this case, you must:
- give the victim an antihistamine: Suprastin, Claritin, Zirtek;
- provide access to fresh air, unfasten clothing;
- call an ambulance.
All other diagnostic and therapeutic measures are carried out only in a hospital setting.

Tip. A live parasite can be stored in the refrigerator for no longer than a day, and moved at normal air temperature. It is better to put crushed during removal in ice.
Pass the tick for analysis You can in the SES, the center of Rospotrebnadzor or the serological laboratory at a medical institution. You can find out the addresses and phone numbers of parasite reception centers at the city polyclinic registry. Analyzes are carried out for a fee, the price of research depends on the region.
If the tick could not be kept alive, for early diagnosis of the disease it is recommended to donate blood for the detection of immunoglobulins for infections. The analysis is carried out quickly, the result is usually ready in 5-6 hours. If there was a vaccination, when giving blood, you must specify its date. The presence of vaccine antibodies can be misleading to healthcare providers.
Tick Bite Disease
So, what is a tick bite dangerous for a person? Infections carried by bloodsuckers can be of a microbial, viral, rickettsial or protozoal nature. All of them cause serious illnesses, often ending in disability, in rare cases fatal. The cause of irreparable disorders in the body is the late detection of the parasite and untimely therapy.
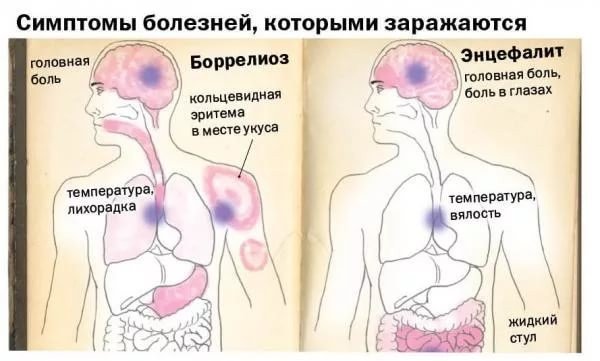
For Russia, the most significant diseases from a tick bite are tick-borne encephalitis, Lyme borreliosis and zoonotic infections. Let's consider them a little more in detail.
Tick-borne encephalitis
The main carrier of this ailment is the ixodid tick.In the wild, the pathogen circulates between bloodsuckers and small animals, usually rodents and birds. In territories developed by man, livestock, cows and goats, becomes an additional reservoir. The causative agent of tick-borne encephalitis persists in parasites for a long time and passes to the offspring through the eggs.
Attention. Virus infection occurs through a tick bite. Often the transmission of the pathogen is recorded through an alimentary route - through infected cow or goat milk that has not been boiled.
The asymptomatic course of the disease is very common and can reach 85–90% in some foci. Prolonged bloodsucking significantly increases the risk of pronounced forms of pathology. The virus tolerates low temperatures well, but dies quite quickly when heated to 80 ° C.
Tick-borne encephalitis infection is seasonal. The first peak of the disease occurs in May-June, the second is recorded in August - early September.
During a bite, the pathogen immediately enters the human blood through the salivary glands of the tick, where it is in the highest concentration. After a few hours, the virus enters the central nervous system of the victim, and after 2 days it can be detected in the brain tissue. The incubation period of encephalitis with a tick bite is 14-21 days, with infection through milk - no more than a week.
Tick-borne encephalitis symptoms
In most victims, an asymptomatic form of infection is recorded, and only 5% have a pronounced form. Tick-borne encephalitis most often begins suddenly with the manifestation of the following symptoms:
- elevated to 39–40 ° C body temperature;
- Strong headache;
- sleep disturbance;
- nausea leading to vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- redness of the skin of the face and upper body;
- weakness, decreased performance.
Such symptoms are characteristic of a febrile form of the disease, which disappears after 5 days. Damage to the central nervous system in this case is absent.
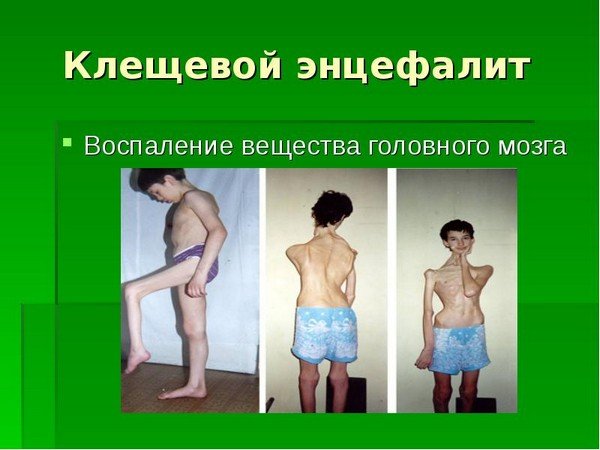
Meningeal and meningoencephalitic forms of pathology are much more severe. The patient complains of lethargy, apathy and drowsiness. Hallucinations, delusions, impaired consciousness, convulsions like epileptic seizures appear. Meningoencephalitic form can be fatal, which is very rare in recent years.
Periodic muscle twitching indicates damage to the peripheral nerves. A polyradiculoneuritis form of encephalitis develops, in which general sensitivity is impaired. With the polioencephalomyelitis form of the disease, paresis of the arms and legs is observed.
Lyme Disease (Lyme Borreliosis)
Borreliosis distributed in the northern regions of Russia. The causative agent enters the bloodstream with a bite of ixodid ticks and can persist in the body for years. The first symptoms of the disease include:
- headaches;
- temperature increase to 38–39 ° C;
- fatigue, weakness and apathy.
1-3 weeks after a tick bite, a seal and annular erythema appear on the site of suction, which can reach 20-50 cm in diameter.
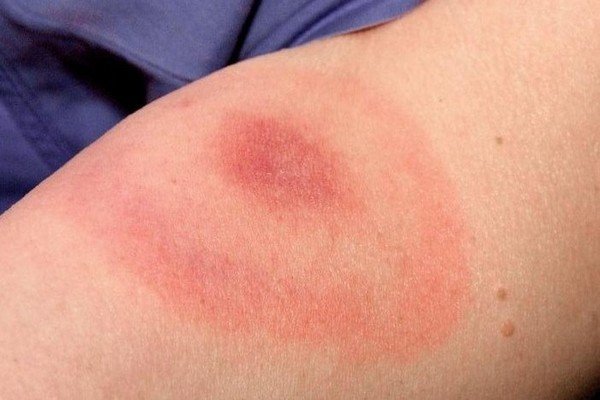
Attention. Despite the fact that a few weeks after the bite, the red spot disappears without a trace, it is necessary to analyze for the presence of the causative agent of Lyme borreliosis, since the disease has serious complications and can be transmitted from a pregnant woman to a child.
Often the central nervous system, heart, muscles and ligaments, joints and organs of vision are involved in the pathological process. Late diagnosis and untimely therapy can lead to the chronicity of borreliosis, which often ends in disability.
Ehrlichiosis
The disease is also transmitted by ixodid ticks. Deer are considered the main reservoir of Ehrlichia, and dogs and horses are intermediate.
The virus enters the human body during a bite with the saliva of a parasite.The incubation period can be up to 3 weeks, and the acute form of the disease lasts 14-21 days. In some cases, the pronounced phase is delayed up to 6-8 weeks.
Ehrlichiosis can be asymptomatic, so clinically bright, even fatal. Common signs of the disease include:
- fever
- increased sweating;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- nausea up to vomiting;
- rigor.
In the acute phase of ehrlichiosis, anemia is observed, a decrease in the level of platelets and white blood cells in the blood.
Tick-borne relapsing fever
Infection is usually registered in the south of Russia, in Armenia, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Georgia and Kyrgyzstan. The disease always occurs suddenly and begins with a vesicle at the site of a tick bite. Then other symptoms are added to the skin manifestations:
- fever;
- fever;
- joint aches;
- nausea and vomiting;
- headache.
Gradually, the bubble becomes a bright red color, a pronounced rash appears on the patient's body, the liver enlarges, the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow.
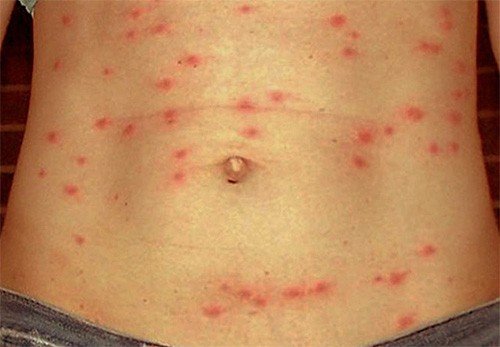
The disease is wave-like. The acute phase usually lasts from 3 to 5 days, then the condition of the victim comes back to normal, the temperature drops. After a few days, everything repeats again. There can be many such attacks. Each subsequent proceeds with less severity.
Coxiellosis
This is one of the most common zoonotic infections in the world. The carrier of the disease can be both farm animals and wild ones. One of the pathogens is a tick, most often ixodid. He is able to maintain rickettsia in the body for a long time and pass it on to offspring. The first symptoms appear 5-30 days after a tick bite:
- increased sweating;
- fever;
- dry, exhausting cough;
- loss of appetite;
- redness of the face and upper body;
- migraines, weakness and drowsiness.
Often, KU fever is accompanied by pneumonia, back pain and muscle pain. The temperature in the early days of the disease can vary during the day several times. Such a disease is treated only in a hospital setting, therapy lends itself well and recovery comes quickly. Complications are rare, the outcome of the disease is most often favorable. Persons with coxiellosis develop stable immunity.
Treatment for tick bite victims
If a tick is bitten and infection is detected according to the results of the analyzes, the patient is given immunotherapy based on the doctor’s prescriptions. Further treatment depends on the type of pathogen that has entered the body.
Therapy of tick-borne encephalitis patients
Specific methods for the treatment of tick-borne encephalitis today do not exist. If there are signs of damage to the central nervous system, the victim must be hospitalized to provide him with medical care. The treatment regimen includes:
- Bed rest during the entire time of the fever and a week after its completion.
- In the early days of the disease, the introduction of immunoglobulin is indicated. To achieve the best result, it is necessary to apply the product as soon as possible, preferably in the first three days after a tick bite.
- In general cases, the patient is prescribed corticosteroid drugs, blood substitutes.
- When meningitis is administered, increased doses of vitamins B and C.
- If respiratory function worsens, the victim is shown mechanical ventilation.
In the recovery period, the patient is prescribed nootropics, tranquilizers and mock testosterone.
Antibiotics may be prescribed as an adjunct to the main treatment for a bite victim. Antimicrobial drugs are used to suppress pathogenic microflora, which can cause various complications.
Therapy of patients with borreliosis
Treatment for Lyme borreliosis involves taking antibiotics. They are used to suppress spirochetes - pathogens. The most commonly used drugs are the penicillin series and cephalosporins.For the relief of erythema, antimicrobial agents of the tetracycline group are prescribed.
When neurological disorders occur, the victim is hospitalized. In the hospital, complex therapy is carried out, including:
- blood substitutes;
- corticosteroids;
- testosterone simulators;
- nootropic drugs to improve cerebral circulation;
- vitamin complexes.
The outcome of borreliosis depends on the timely detection of a tick bite, the correct diagnosis and the early initiation of therapy. Illiterate treatment often leads to the chronic phase of Lyme disease, which stops with great difficulty and can result in disability or death of the victim.
Attention. For the treatment of protozoal infections, drugs are used that exclude the further growth and development of protozoa.
Complications after a tick bite
Summarizing all of the above, it is possible to draw a very disappointing conclusion about the consequences of a tick bite. As you can see, infections affect the most important body systems:
- lungs - with the development of symptoms of pneumonia and pulmonary hemorrhage;
- liver - there is a digestive disorder, problems with stool (diarrhea);
- CNS - with frequent headaches, hallucinations, paresis and paralysis;
- cardiovascular system - arrhythmia appears, jumps in blood pressure;
- joints - arthritis and arthralgia are formed.
The consequences of a tick bite can develop in two ways. With a favorable outcome, loss of working capacity, weakness and lethargy lasts 2-3 months, then all body functions are normalized.
With an ailment of moderate severity, recovery lasts up to six months or longer. A serious form of the disease requires a rehabilitation period of up to 2-3 years, provided that the disease progressed without paralysis and paresis.
With an unfavorable outcome, there is a persistent and prolonged (or constant) decrease in the quality of life of the tick bite victim. It is manifested by a violation of motor function. The clinical picture worsens significantly under the influence of nervous and physical overwork, pregnancy, regular intake of alcohol.
Persistent violations in the form of epileptic manifestations and spontaneous convulsions lead to the patient's disability.
Disability as a result of a tick bite
As you know, there are 3 groups of disabilities. The degree of damage to the body after a tick bite is determined by a special medical commission:
- Disability of the III group - mild paresis of the hands and feet, rare epileptic seizures, the inability to perform highly qualified and requiring precision and attention work.
- Disability of the II group - bright paresis of the limbs, partial paresis of the muscles, severe epilepsy with a change in the psyche, asthenic syndrome, loss of self-care ability.
- Group I disability - acquired dementia, severe impaired motor function, persistent and complete epilepsy, widespread muscle paresis, loss of self-control and the impossibility of independent movement.
In severe cases, with inadequate treatment of infections caused by a tick bite or complete absence of therapy, a fatal outcome is possible.
Tick bite prevention
The main and main measure for the prevention of diseases transmitted by bloodsuckers is vaccination. The event significantly reduces the risk of infection after tick bites. Vaccination is necessary for people living in epidemiologically hazardous areas or people whose work is related to forestry.
Tip. Despite the limited risk group, vaccination is best done by everyone. After all, it is not known where "lucky" to meet with a tick.
Primary vaccination is allowed from an early age. Adults can use domestic and imported drugs, for children - only imported ones. They should not buy the vaccine themselves and bring them to the vaccination room. All the same, they will not drive her.The drug requires very strict storage rules, compliance with a certain temperature and light conditions, which is impossible to do at home. Therefore, it makes no sense to purchase an expensive drug and store it in the refrigerator.
There are two vaccination options:
- Preventive vaccination. Helps protect against tick bites during the year, and after additional vaccination - at least 3 years. Revaccinations are carried out every three years.
- Emergency vaccination. Allows you to protect yourself from tick bites for a short time. For example, such a procedure will be necessary for urgent trips to regions with high tick activity. While in epidemiologically hazardous areas, iodantipyrine is recommended.
The introduction of the vaccine is carried out only after a detailed survey, visual inspection and temperature measurement. Persons with inflammatory diseases are not vaccinated until they recover completely.
How to protect yourself from a tick bite?
Going to an unfavorable zone, you should choose clothes of light colors:
- a shirt or jacket with cuffs and a tight-fitting collar, trousers tucked into boots;
- Encephalitis suit;
- dense hood with ties that protects the ears and neck from ticks;
- clothing should preferably be treated with insecticides.
During hiking, it is recommended to avoid ravines and tall grass, it is better to go in the middle of the path. After leaving the forest, you must carefully examine yourself for ticks. In this case, it becomes possible to detect and remove the parasite before a bite.

To repel mites, special insecticides based on DETA are available, but repellents are not effective enough and require application every 2 hours. They can handle open areas of the body and clothes.
Acaricides are more effective. Drugs are used for contact destruction of ticks. They can only be processed with outerwear worn on underwear.
Attention. Often on sale there are acaricides for application to the skin. However, they should be used very carefully. A severe allergic reaction and poisoning are possible.
Tick-borne encephalitis insurance
Recently, insurance of expenses associated with a possible encephalitis disease after a “meeting” with a tick has become widespread. Such a measure is often used as an adjunct to vaccination or as an independent event.

Insurance will help pay for the costly treatment of tick-borne encephalitis and other infections carried by bloodsuckers.
The irreparable consequences of a tick bite can be prevented if you seek medical help on time and start treatment. Remember, a sucking parasite does not immediately transmit the infection. The longer it is on the body, the greater the risk of contracting tick-borne encephalitis or Lyme borreliosis.
Attention. The article is for reference only. Competent diagnosis and treatment of diseases is possible only under the supervision of a specialist.


 (votes: 46, average rating: 4,65 out of 5)
(votes: 46, average rating: 4,65 out of 5)
it’s not clear what to do
It is not clear what to do if the tick bit, but they got it and lost it. What to do ????????? Where to go?
06,05,2019